Introduction
Navigating the world with orthopedic pain poses numerous challenges that can impact all aspects of daily life. Whether it originates from arthritis, bone fractures, or conditions caused by repetitive strain, the pain can impose significant limitations. Finding effective pain management strategies is about alleviating discomfort and regaining control over your lifestyle. Reliable resources such as https://occ-ortho.com/ provide a comprehensive understanding of dealing with such issues, highlighting traditional and innovative pain management practices. The emphasis on non-invasive methods and combined medical interventions offers promising relief options.
Understanding Pain in Orthopedic Conditions
Understanding the nature of pain in orthopedic conditions is crucial for effective treatment. Pain can be acute, chronic, or mechanical. Acute pain occurs after an injury and can last a few minutes to months. Chronic pain persists beyond the healing period and can significantly impact the quality of life. Mechanical pain, often associated with joint motions, arises from physical stressors during activities.
Non-Pharmacological Pain Management Techniques
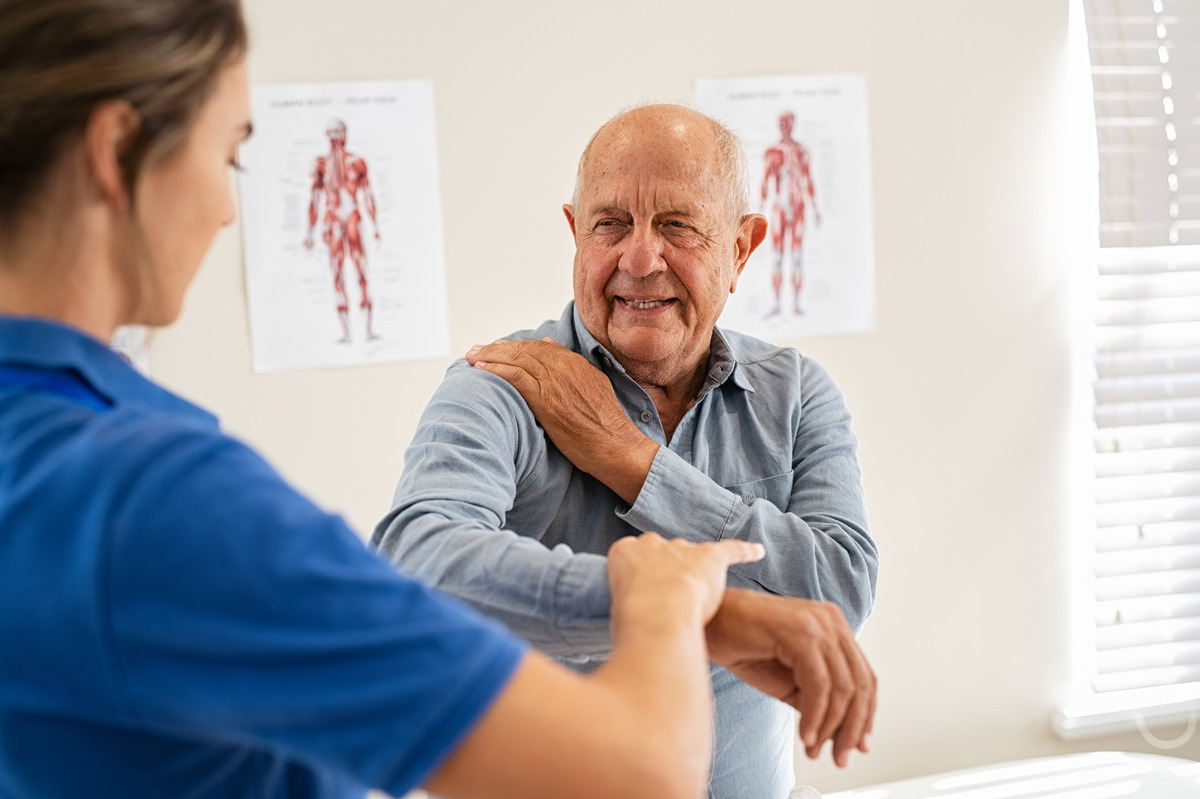
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy stands out as a cornerstone for non-pharmacological pain management. It encompasses a series of exercises that target specific muscle groups, aiming to enhance mobility while minimizing pain. Numerous studies on physical therapy underscore its efficacy in reducing dependence on medication, speeding up the recovery process, and potentially averting the need for surgical intervention. Each physical therapy program is uniquely crafted to address individual requirements, focusing on gradually increasing strength and flexibility to foster resilience against pain.
Exercise and Yoga
Incorporating exercise and yoga into daily routines offers myriad benefits for pain management, extending beyond their physical effects. Regular exercise strengthens muscles, reduces inflammation, and enhances overall endurance. Yoga, in particular, combines physical postures with mindfulness, fostering physical and mental health. It is well-regarded for lowering stress and improving sleep quality, positively influencing pain perception. Adopting a yoga practice can seem daunting at first, but even simple poses can yield substantial improvements in flexibility and pain management over time.
Pharmacological Options for Pain Relief
Medications remain a pivotal component in orthopedic pain management. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and opioids are commonly prescribed to manage moderate to severe pain levels. However, understanding their effects and risks is critical, as these medications are not without side effects. Under the careful guidance of healthcare professionals, these drugs can provide effective temporary relief and be part of a broader pain management plan. Combining pharmacological methods with lifestyle adjustments often leads to more sustainable pain reduction.
The Role of Nutrition in Pain Management
Nutrition is an often overlooked yet significant aspect of pain management. A nutritious diet can help modulate inflammation and speed up the recovery process. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as walnuts and fatty fish, have anti-inflammatory properties that assist in reducing pain perception. Antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables also contribute to reducing inflammation and promoting tissue repair. Vitamins and minerals in whole foods work synergistically to support the body’s natural healing processes, providing a much-needed edge against chronic pain.
Psychological Approaches to Pain Relief
Psychological strategies in pain management acknowledge the intricate link between mind and body. Methods like cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) are crucial for changing how people see chronic pain, which frequently results in significant changes to their overall pain experience. Additionally, practices like meditation and mindfulness encourage relaxation and help patients cultivate resilience against stress, which can amplify pain sensations. Given that chronic pain can often lead to mental challenges such as anxiety and depression, psychological therapies are an invaluable component of holistic pain management.