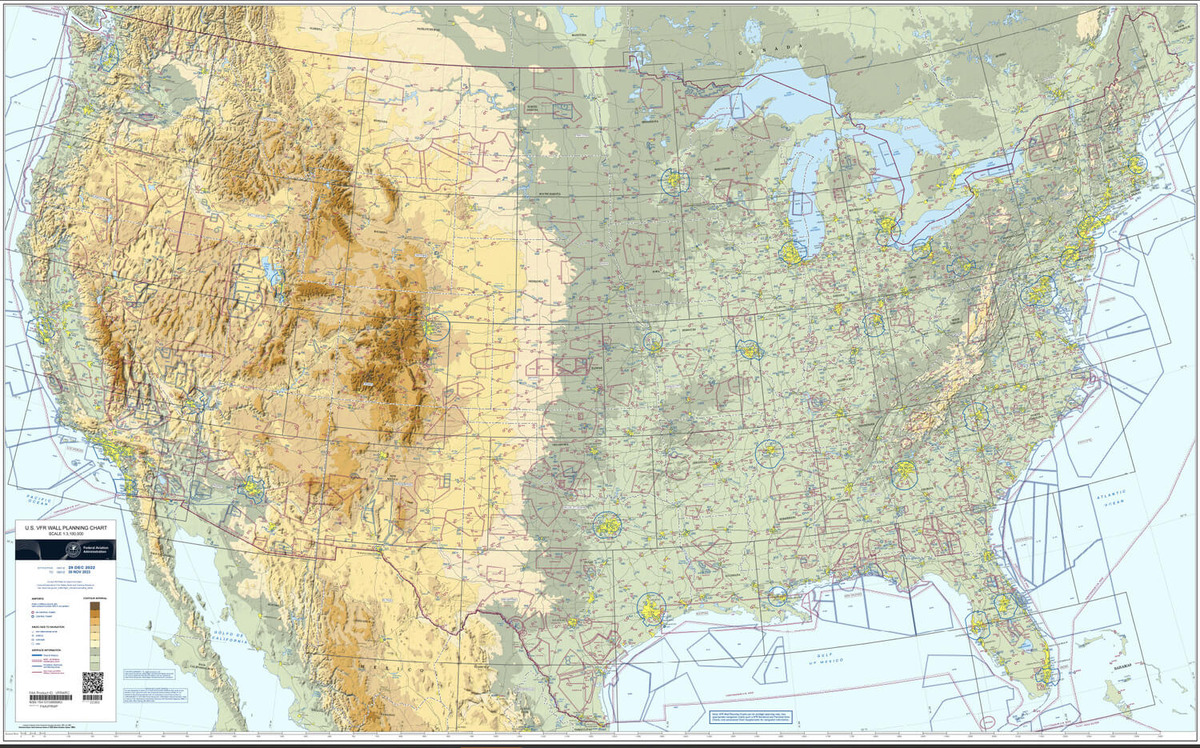
FAA sectional charts are vital tools for pilots, providing critical information for navigation and situational awareness in the skies. Understanding how to read and interpret these charts is essential for safe and efficient flight planning. This comprehensive guide will cover the key aspects of FAA sectional charts, including their features, how to read them, and tips for effective use.
- What Are FAA Sectional Charts?
FAA sectional charts are detailed maps designed specifically for VFR (Visual Flight Rules) navigation. These charts depict various features of the terrain, including topography, airspace classifications, navigational aids, and obstacles, making them indispensable for pilots flying under visual conditions. Sectional charts are updated regularly to reflect changes in airspace, navigational aids, and other critical data.
- Key Features of Sectional Charts
Understanding the key features of sectional charts is crucial for effective navigation. Here are some of the essential elements:
- Topography: Sectional charts include detailed representations of the terrain, such as mountains, valleys, and bodies of water, using contour lines and shading.
- Airspace Classifications: Different types of airspace are depicted using color-coded boundaries. Familiarity with these classifications—Class A, B, C, D, E, and G—is vital for maintaining compliance with regulations.
- Navigational Aids: VORs (VHF Omnidirectional Range), NDBs (Non-Directional Beacons), and other navigational aids are marked on sectional charts, allowing pilots to determine their position and navigate accurately.
- Obstacles: Sectional charts highlight obstacles such as towers, buildings, and terrain features that could pose a hazard during flight. These obstacles are typically shown with height information.
- Communication Frequencies: Frequencies for airports, approach control, and other critical communication points are listed on sectional charts, ensuring pilots can easily access necessary information.
- How to Read FAA Sectional Charts
Reading sectional charts effectively requires familiarity with their symbols, legends, and layout. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Familiarize Yourself with the Legend: Each sectional chart includes a legend that explains the symbols and colors used on the chart. Understanding these symbols is crucial for interpreting the information correctly.
- Identify Your Location: Use landmarks, navigational aids, or GPS to determine your current location on the chart. This helps in assessing your surroundings and planning your route.
- Understand Airspace Boundaries: Pay close attention to the airspace boundaries depicted on the chart. Knowing the altitude limits and entry requirements for each airspace type is essential for safe navigation.
- Assess Terrain and Obstacles: Check the topography and identify any obstacles that may affect your flight path. Pay attention to the heights of obstacles, especially when flying at lower altitudes.
- Plan Your Route: Use the information on the chart to plan your flight route, considering factors such as airspace restrictions, navigational aids, and weather conditions.
- Tips for Effective Use of Sectional Charts
- Stay Updated: Regularly check for updates to sectional charts, as changes in airspace and navigational aids can occur frequently. You can access updated charts through the FAA’s website or other aviation resources.
- Practice Navigation: Use sectional charts during practice flights to improve your skills. The more you work with them, the more comfortable you will become with reading and interpreting the information.
- Combine with Technology: While sectional charts are essential, consider using digital tools and apps that integrate sectional chart data with GPS navigation. This can enhance your situational awareness during flight.
- Use a Checklist: Create a pre-flight checklist that includes verifying the current sectional chart, noting any temporary flight restrictions (TFRs), and ensuring you have all necessary navigational aids.
- Participate in Training: Take part in flight training programs that focus on VFR navigation and the use of sectional charts. Practical experience with instructors can help solidify your understanding.
Conclusion
FAA sectional charts are indispensable tools for pilots, providing critical information for navigation and safety. By understanding the key features of these charts, learning to read them effectively, and following best practices for their use, you can enhance your flying experience and ensure safe navigation in the skies. Regular practice and staying informed will equip you with the skills necessary to master FAA sectional charts and navigate confidently as a pilot.